![]() Sky Series
#
Sky Series
#
A sky series contains both cumulative and over time data about the energy emitted from the sky, at a location during a specified time period. It is used for both radiation and daylight related analyses, usually in combination with a shading mask. See the sky instance for further description about how the sunlight is represented in the sky.
Series Data#
The point in time data in the sky series covers each time step in the specified time pattern. This data is used for analyses that measure conditions over time, like useful daylight illuminance. Each patch for each time step contains the diffuse, direct and total amount of irradiance \(W/m^2\) and illuminance \(cd/m^2\) emitted at the specific point in time.
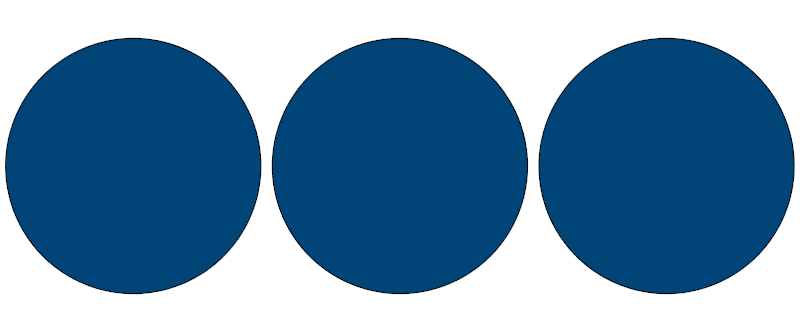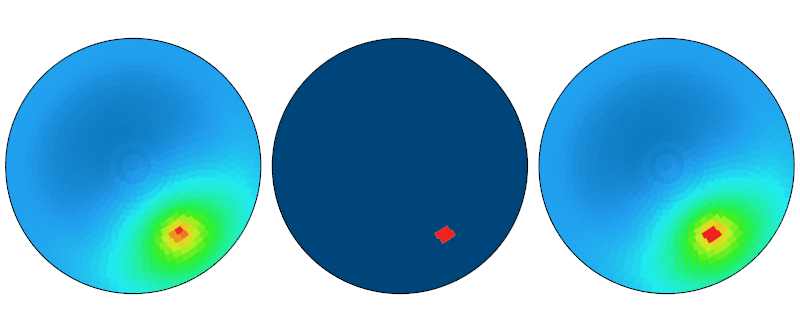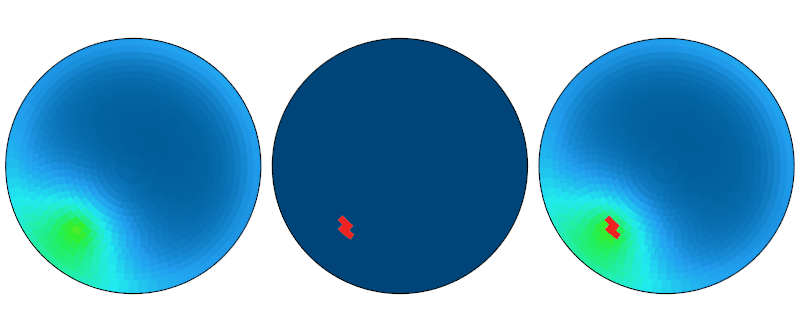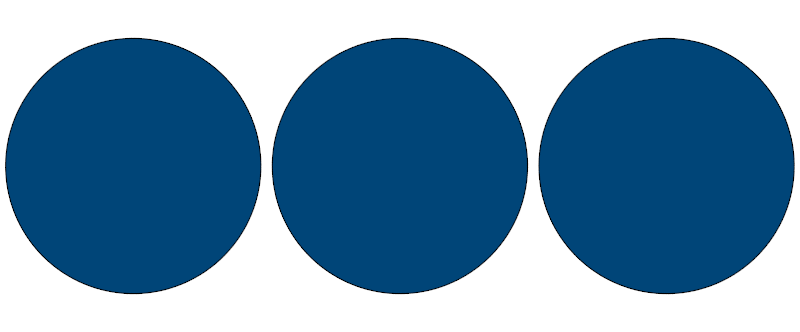
Cumulative Data#
The cumulative data in the sky series is used for analyses that measure total recipience over time, like the cumulative radiation analysis. Each patch contains the diffuse, direct and total amount of irradiation \(Wh/m^2\) and cumulative illuminance \(cd.h/m^2\) emitted over the time span in the time pattern.
Create Sky Series#
Weather#
The weather describes the location specific conditions that will be used to determine the sky conditions. The weather data is measured on an hourly interval and will be interpolated for sub hourly time steps.
Hemisphere#
The hemisphere decides the subdivision of the sky dome and thereby the amount of patches that should be used to describe the sky conditions. More patches produce a higher resolution and
thereby a more accurate interpretation of the sky but will also lead to longer analysis times.
Time Pattern#
The time pattern specifies the points in time that will be sampled in the sky series. The amount of time steps in the time pattern will decide the amount of skies sampled per hour and thereby greatly affect the time based resolution, especially for the directional factor.
Ground Reflectance#
A value between 0 and 1 indicating the fraction of light that is reflected by an artificial ground plane. This is used to decide the contribution form parts of the lower hemisphere that are visible to the analysis.
Warning
It is still important to model ground and context to ensure valid results.
Luminance Distribution Model#
A luminance distribution model is used to calculate the irradiance and illuminance contribution from each patch in the sky. There are two available models with slight differences. For a detailed breakdown of the equations behind them, Andrew Marsh provides an excellent overview in his article Sky Distribution Equations.
CIE Standard Sky Model#
The CIE Standard Sky Model published in 2002 uses an updated version of the All-Weather Sky Model and was adopted by ISO/CIE for calculating the CIE Standard General Sky.
All-Weather Sky Model#
The All-Weather Sky Model uses the traditional Perez equations published in 1993 to calculate the luminance distribution. This model is used in many other popular daylighting softwares.
- Darula, Stanislav & Kittler, Richard. (2002). CIE general sky standard defining luminance distributions. Proc. Conf. eSim 2002, Montreal, Canada.
- R. Perez, R. Seals, J. Michalsky, All-weather model for sky luminance distribution—Preliminary configuration and validation, Solar Energy, Volume 50, Issue 3, 1993, Pages 235-245